Automation of manual processes: Your blueprint for scaling without breaking
Manual processes drain your team’s time and create costly errors—which is why 71% of companies prioritize automation in 2025, according to Celigo’s Intelligent Automation Benchmark Report. Organizations automating high-friction workflows reported 30-50% fewer in maintenance hours and up to 65% fewer errors in financial processes.
Yet 84% of IT leaders say integration complexity is slowing their growth. The right automation foundation makes the difference—companies that approach it strategically unlock exponential gains.
This guide shows you how to identify which manual processes are costing you the most, prioritize automated business processes strategically, and build a platform approach that scales with your business.
What is manual process automation?
Manual process automation connects disparate systems through integration workflows that orchestrate data movement, transformation, and validation across applications. It replaces multi-step processes that previously required manual coordination, data re-entry, and cross-system reconciliation.
The process involves:
- Mapping current workflows with manual handoffs and bottlenecks
- Identifying all impacted systems, teams, and data flows
- Determining your system of record (ERP for finance, CRM for sales)
- Defining the optimized automated workflow
- Configuring integrations that orchestrate data movement between systems
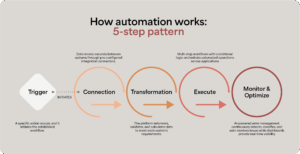
How automation works
At its core, automation follows a pattern once established:
- Trigger: A specific action occurs, and it initiates the established workflow.
- Connection: Data moves securely between systems through pre-configured integration connectors.
- Transformation: The platform reformats, validates, and calculates data to meet each system’s requirements.
- Execute: Multi-step workflows with conditional logic orchestrate automated operations across applications
- Monitor & Optimize: AI-powered error management continuously detects, classifies, and auto-resolves issues while dashboards provide real-time visibility
Key benefits of automating manual processes
Automating manual processes delivers measurable improvements across your organization:
- Time savings: Teams reclaim hours previously spent on manual tasks like data entry, allowing them to focus on work that requires human judgment and creativity.
- Error reduction: Automated workflows eliminate manual mistakes from copy-paste operations.
- Scalability: Handle higher transaction volume during peak periods without proportional headcount increases, enabling growth without operational bottlenecks.
- Cost efficiency: Reduce maintenance overhead while avoiding the need to hire additional staff just to maintain current operations at higher volumes.
- Auditability and visibility: Automated audit trails and real-time monitoring provide complete transparency into every transaction and workflow, enabling teams to trace issues, verify data accuracy, and maintain detailed records for compliance..
Types of manual process automation
An automation strategy addresses five distinct integration patterns, each designed to solve specific operational challenges:
- Application integration: Connects cloud-based business applications (ERP, CRM, ecommerce platforms, marketing tools) to synchronize data and trigger actions across systems.
- Data integration: Consolidates data from multiple sources into data warehouses for analytics and reporting, then syncs modeled insights back to operational systems through ELT and reverse ETL pipelines.
- Workflow automation: Orchestrates multi-step processes that span departments and systems—like order-to-cash flows that touch sales, finance, operations, and customer success.
- File-based automation: Handles documents, CSV imports/exports, and other structured data that still moves between systems in file formats rather than APIs.
- EDI transaction automation: Exchanges standardized business documents (purchase orders, invoices, advance ship notices) with trading partners and retailers electronically, eliminating manual document handling while ensuring compliance with partner requirements and industry standards like X12 and EDIFACT.
- API management: Builds, secures, and governs APIs that expose your business data and processes to external partners, internal teams, or third-party developers, providing centralized control over access and policy enforcement.
Businesses that leverage automation most successfully do so through multiple types of connections instead of creating point-to-point connections.
The question is whether you manage them through a unified platform or cobble together point solutions that create their own complexity. Choosing a single automation platform that provides an end-to-end solution and prevents complicated integrations is ideal.
Common manual processes to automate
You don’t need to automate everything at once, but understanding what’s possible helps you prioritize high-impact opportunities and ensure that you’re thinking about a unified, cohesive system that you can build upon.
While there are plenty of different manual processes your team can automate, here are three high-impact automations that can benefit most scaling businesses.
1. Order-to-cash automation for ecommerce operations
Ecommerce companies managing multiple sales channels struggle to balance constant manual work. Operations teams monitor each platform separately, manually enter orders into the ERP, check inventory across warehouses, create shipping labels, and update inventory everywhere.
Automation connects all sales channels to your ERP and fulfillment systems:
- Orders flow automatically.
- Inventory syncs in real-time to prevent overselling.
- The system routes each order to optimal fulfillment locations.
- Customers receive tracking updates without manual intervention.
- Returns are processed automatically through the reverse workflow.
The result: Operations teams handle more order volume without adding headcount, errors drop, and inventory accuracy stays consistently high even during seasonal shopping spikes.
→ See how Celigo automates order-to-cash workflows with prebuilt connectors for ecommerce platforms like Shopify, Amazon, Walmart, and more. Schedule a demo.
2. Financial close acceleration for SaaS companies
SaaS finance teams manually collect data from billing platforms, CRM systems, data warehouses, and CPQ tools just to close the books.
Manual processes involve someone exporting data from each system, reconciling discrepancies, calculating revenue recognition, and creating journal entries.
Automation connects billing, CRM, and ERP systems to eliminate manual data entry and collection:
- Data flows on your schedule, which can be daily, weekly, or in real-time.
- Revenue recognition calculates automatically based on contract terms.
- Journal entries generate without manual intervention.
- Discrepancies trigger immediate alerts instead of surprise discoveries weeks later.
- Complete audit trails maintain compliance for SOX and other requirements.
The result: Close time drops from weeks to days, finance teams focus on analysis instead of data collection, and leadership gets accurate financial visibility when they need it.
→ Learn more about Celigo’s financial automation solutions.
3. Employee onboarding and IT provisioning automation
When employees start, HR creates records while IT manually provisions accounts across complicated tech stacks.
Each step involves tickets and email threads, and new employees wait days for access while tasks get forgotten. Then, during offboarding, manually revoking access across dozens of systems becomes a security risk.
Automation connects HR systems to IT provisioning tools:
- Accounts are created with appropriate role-based permissions when HR marks someone as hired.
- Laptop orders go to procurement automatically.
- Facilities receive badge requests without manual coordination.
- Managers get Day 1 task lists and reminders.
- One status change triggers immediate deactivation everywhere during offboarding.
The result: New employees arrive on their first day with everything ready, security improves through comprehensive immediate offboarding, and IT teams focus on strategic work instead of repetitive account management.
→ Explore Celigo’s Employee onboarding automation.
5 steps to automate a manual process
The right framework helps you build your automation roadmap strategically rather than reactively, creating a strong and buildable foundation.

Step 1: Map your operational breaking points
Start by identifying where manual processes are actively failing or creating risk right now. Look for these warning signs:
- Volume triggers: Which processes slow down or fail when transaction volume increases? You may notice that peak season order processing is inefficient, or that month-end financial close has your team working overtime.
- Error hot spots: Where do mistakes consistently occur due to manual data entry or copy-paste between systems?
- Customer-facing friction: Which manual handoffs delay customer onboarding, order fulfillment, or support resolution?
- Compliance exposure: What manual processes create audit risks or regulatory concerns?
- Scaling blockers: Where would you need to hire additional headcount just to maintain current operations?
Pro tip: Talk to the teams doing the work. They know which processes are breaking and where the hidden time drains exist. This is where to start automating manual tasks.
Step 2: Calculate the true cost of staying manual
Most organizations underestimate what their manual processes are actually costing them. Build a business case by quantifying these costs:
Direct time cost: Calculate this by multiplying the hours per week spent on the process by hourly rates and number of people involved. Include execution time, error correction, follow-up, and coordination across teams.
Error cost: Calculate the costs associated with customer credits for late shipments, compliance penalties for audit findings, lost deals from quote errors, and rush fees to fix mistakes.
Opportunity cost: Calculate the cost of strategic work that isn’t happening because your team is stuck on manual tasks. For example, operations could optimize processes instead of re-keying orders, and IT could enable new capabilities instead of provisioning accounts.
Scaling cost: Calculate the additional headcount needed to handle increased volume at your target growth rate, multiplied by loaded annual cost (which is typically 1.3-1.5x salary).

Step 3: Prioritize using the impact-effort matrix
Not all automations deliver equal value, so it’s important to sequence your roadmap strategically.
1. Quick wins
You want to start with quick wins to build momentum and demonstrate value quickly.
These will have high business impact and low technical complexity, and should include well-defined, repetitive processes with clear rules that don’t require human judgement. Ideally, they should also be processes where prebuilt connectors exist for your core systems.
Examples include:
- Order-to-cash workflows
- CRM-ERP synchronization
- Employee onboarding and offboarding with IT provisioning
2. Strategic automations
Strategic automations will have a high business impact, but be moderately complex. They may involve cross-departmental processes that require coordination between teams or customer-facing workflows that impact experience.
These deliver substantial value but require more planning, testing, and change management than quick wins.
Examples include:
- Financial consolidation across entities
- EDI integration with retail partners
- Subscription renewal forecasting
3. Advanced optimizations
Advanced automations involve processes requiring custom logic, complex data transformations, or AI capabilities. These include multi-entity operations, legacy system modernization, or lower-volume but high-complexity workflows. As a result, tackle these once your foundation is solid.
Build these once Tier 1 and Tier 2 automations are delivering value and you’ve established platform expertise. The early wins create organizational momentum and prove the platform’s capabilities before tackling these more complex scenarios.
Examples include:
- AI-powered document processing and classification
- Custom data pipelines with complex business rules
- Legacy system integration requiring extensive transformation logic
Step 4: Audit your integration landscape
Before adding new automation, understand what you already have. Most companies discover they have more integrations than they realized, and that some integrations are causing more problems than they’re fixing.
Create an inventory with these steps:
- List all cloud applications: Identify all cloud applications, ERPs, and data sources currently in use. Most mid-market companies have at least 20 tools in their tech stack.
- Document existing integrations: Identify point-to-point connections, custom code, CSV imports/exports, and manual processes that trigger simple automations.
- Identify integration debt: Look for brittle connections requiring constant maintenance, undocumented custom code, or workflows that depend on specific individuals who might leave.
- Map coverage gaps: Determine which systems should connect but are currently still disjointed.
This audit reveals two critical insights:
- Where automation or tech sprawl is creating new problems that a unified automation platform could solve
- Which manual processes are actually ready for automation, compared to which processes may need improvement first
You might discover that you’re paying for multiple integration tools that overlap in capability, or that a custom integration built three years ago is actually breaking regularly but nobody wants to touch it because the original developer left. These discoveries inform your platform strategy.
Step 5: Choose a platform strategy, not point solutions
The biggest mistake organizations make is solving integration problems one at a time with disjointed, disconnected tools. The need for extensive and increasingly complicated integrations becomes more challenging and expensive as you scale.
Choosing a single platform for your automation strategy yields the following benefits:
- Reusable components: Build a strategy once and then deploy it across multiple use cases.
- Consistent governance: Centralize monitoring, security, and compliance in one place.
- Predictable costs: Avoid transaction-based pricing that scales unpredictably.
- Faster time-to-value: Leverage prebuilt connectors and templates instead of starting from scratch every time.
When choosing an automation platform look for the following:
- Prebuilt connectors for your core business applications, including your ERP, CRM, ecommerce, and HR systems
- Visual workflow builder that’s intuitive to both IT and non-technical business users
- Built-in error management and monitoring at the platform level, not individual workflows
- Transparent, predictable pricing that doesn’t penalize growth
- Security certifications and compliance capabilities for your industry, potentially including SOX, HIPAA, and GDPR guidelines
Building your automation advantage
Automation transforms how businesses operate. When done right, it touches every department. Finance accelerates their close, Operations handles order spikes on Amazon Prime Day, IT provisions employees in minutes instead of days, and sales teams work from real-time data instead of stale exports.
Think about your business a year from now. Manual processes that barely work today will break completely under increased load. The question isn’t whether to automate, it’s whether you’ll build on a foundation that enables sustainable growth.
→ Ready to identify which manual processes are holding your business back? Schedule a demo to see how Celigo automates processes across finance, operations, IT, and beyond.