7 data integration challenges (and how to solve them)

Your team scopes a data integration project: two weeks, one developer, ERP to warehouse. Six weeks later, you’re still troubleshooting.
The “simple” ERP connection actually pulls from seven systems. Half the source data has duplicates, missing fields, and formatting issues. The custom script works—until Black Friday traffic hits 50x normal volume and fails spectacularly.
Finance wants to know why their dashboards haven’t updated in three days.
This happens every week. Projects stretch from weeks to months. Budgets double. Integrations break during quarter-end close, peak season, and board meetings—exactly when executives need the data.
The problem isn’t the technology. It’s underestimating seven specific challenges that derail even well-planned projects. Here’s what goes wrong—and how to prevent it.
What is data integration?
Data integration is the process of combining data from multiple sources to create unified, actionable insights across your organization.
Modern data integration uses ELT (Extract, Load, Transform). It extracts data from sources, loads it directly into cloud data warehouses like Snowflake or BigQuery, and then transforms it using the warehouse’s computing power.
This replaced legacy ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) methods that required heavy data preparation and complex transformations before data reached the warehouse.

Cloud data warehouses changed the game by offering massive processing capabilities that make in-warehouse transformation faster and more flexible than older approaches.
Modern platforms like Celigo support reverse ETL—moving transformed data from warehouses back into operational systems, turning your data warehouse into both a reporting destination and a distribution hub.
What makes data integration so challenging?
Data integration looks deceptively simple on paper: you move data from System A to System B, and you’re done.
Reality proves far more complex, with multiple systems requiring synchronization, conflicting data formats, emerging real-time requirements, and unexpected governance demands.
What begins as a “simple” use case quickly reveals dependency chains, system-of-record questions, and edge cases nobody anticipated during planning.
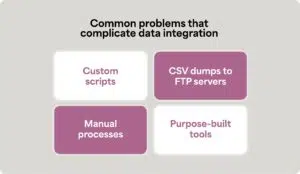
Failed approaches are common:
- Custom scripts that break when APIs change
- CSV dumps to FTP servers requiring manual intervention
- Manual processes that don’t scale with business growth
- Purpose-built tools that solve only part of the problem
Organizations need strategic approaches, not tactical band-aids. Understanding the challenges below helps you build data integration infrastructure that scales rather than breaks under pressure.
7 data integration challenges
Here are the seven most common challenges that derail data integration projects and practical solutions for overcoming each one.
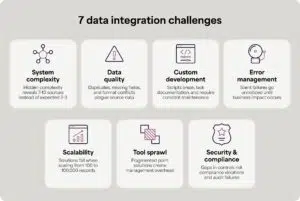
1. Underestimating system complexity and data sources
Organizations think they need data from two to three systems, when in reality, their existing infrastructure is already more complex than they realized… and they need seven to 10 sources instead.
Why this happens:
Incomplete requirements mapping means teams don’t identify the true system of record for each data element. They start implementation, then discover dependencies mid-project that weren’t part of the original scope.
Real-world example:
Your team starts by thinking they only need to get just your ERP data to the data warehouse.
Then you realize sales data lives in the CRM, customer service data sits in a separate system, inventory comes from warehouse management, and financial data splits across the ERP and billing platform.
Each discovery adds weeks to the timeline and complexity to the architecture.
Business impact:
- Project scope creep and timeline delays
- Budget overruns as requirements expand
- Incomplete reporting that doesn’t answer business questions
- Frustrated stakeholders who expected faster results
The solution:
- Conduct a thorough data source audit before starting implementation, and map business requirements back to the system of record for each data element.
- Plan for iterative implementation that can accommodate discovery.
- Choose a platform that grows with complexity rather than requiring architectural rewrites when new sources emerge. Celigo’s data integration features work alongside our other advanced automation solutions.
2. Data quality and consistency issues
Source system data isn’t integration-ready. Duplicates exist, required fields are missing, and formats conflict between systems created by years of manual data entry.
Why this happens:
Legacy systems lack proper validation, and there’s unlikely to be data governance in existing source systems. Some organizations operate for years without standardization practices, and integration projects are what expose the accumulated mess.
Real-world example:
NetSuite says contact “Karen Smith” already exists, but there are actually three different “Karen Smith” entries with slight variations in spelling or formatting. Your CRM treats these as three different Karen Smiths, even though they’re all the same person—and so they’re stored as three different people in the data warehouse, giving your team faulty data.
The perception problem:
Organizations expect integration platforms to automatically fix data quality issues. They don’t.
Integration platforms move data and apply transformations, but they can’t resolve fundamental data hygiene problems that require business decisions about which record is correct.
Business impact:
- Delayed go-live while cleaning source data
- Ongoing maintenance burden managing exceptions
- Lost confidence in reporting accuracy
The solution:
- Run pre-integration data quality assessments
- Clean source data before deployment
- Build validation rules into workflows that catch problems early
- Document data requirements clearly once you create standardized processes
3. Failed custom development approaches
Custom scripts seem economical initially, but then they break, require constant maintenance, and lack documentation that explains how they actually work. This can be a nightmare when they’re used for data integration purposes.
Why this happens:
The “we’ll just build it ourselves” mindset underestimates ongoing maintenance.
Contractors build solutions then leave without documentation, and developers write code without error handling or monitoring. And now, increasingly, AI-generated code “sort of works,” but nobody can explain the logic when issues arise.
Real-world scenarios:
Teams dump CSV files to FTP servers and manually process them. This is tedious, mistake-prone, and unreliable.
Developers write direct API calls without error handling, so when the API changes, everything breaks, and cron jobs run custom scripts that fail quietly in the background.
Nobody realizes anything’s wrong until the CEO asks why the dashboard hasn’t been updated. Or, there’s the classic scenario: it worked perfectly for six months, then suddenly stopped, and nobody can figure out why.
Business impact:
- Executives discover missing data when asking business questions
- No audit trail or error visibility
- Complete dependency on specific developers
- Can’t scale efficiently with business growth
- Security and compliance risks from undocumented processes
The solution:
- Instead of custom code, use a dedicated data integration platform with built-in error management, governance, version control, and visual workflow documentation features
- Transfer knowledge from developers to operators who manage day-to-day execution
- Create clear documentation about how your systems work
4. Inadequate error management and monitoring
Workflows fail silently, errors go unnoticed, and when problems are finally caught, they require extensive manual cleanup from overwhelmed IT teams.
As workflows become business-critical, error management transforms from technical features to revenue protection. When executives rely on dashboards for decision-making, missing data creates business risk. When financial reporting depends on automated data consolidation, errors delay month-end close.
Why this happens:
There are multiple reasons why this happens:
- Proactive monitoring doesn’t exist
- Simple logging doesn’t provide actionable resolution paths
- Alert fatigue from too many notifications results in teams accidentally ignoring warnings
- There’s no classification to distinguish routine errors from critical issues
- Data integration platforms that are missing critical features like resolution workflows or automatic recovery capabilities
Real-world scenarios:
Your data flow hits Snowflake’s API rate limit and stops dead. Someone has to manually restart it. Snowflake goes down for scheduled maintenance, and ten different flows fail.
Each one needs manual attention to get running again, and then errors pile up overnight. When your team arrives in the morning, there are hundreds waiting to be fixed. Picture an IT person staring at their screen, facing the task of manually resolving hundreds of errors from a single system outage.
Business impact:
- Lost business from incomplete data
- Weekend and evening emergency calls
- Lack of confidence in automated workflows
- Wasted time on preventable manual work
The solution:
- Use data integration platforms which leverages AI-powered error management and resolution.
- Implement automatic recovery workflows that handle API throttling (auto-pause, wait, restart), system downtime (queue flows, monitor availability, resume automatically), and rate limiting (intelligent throttling)
- Set up full lifecycle error management where you can review, modify payloads, retry, dismiss, or assign errors to team members
- Create proactive alerting that notifies teams without overwhelming them with noise
The key differentiator is treating errors as important issues that need complete lifecycle management, not afterthoughts that require constant manual intervention.
5. Scalability and performance requirements
Solutions that work perfectly for 100 records fail at 100,000 records, leaving organizations scrambling during their busiest business periods. What seemed adequate in testing becomes a disaster in production.
Why this happens:
Testing environments use sample data, not production volumes. Single-threaded processing can’t handle real loads, API rate limits weren’t considered during planning, and teams didn’t anticipate Black Friday traffic or month-end close volume.
Real-world scenarios:
Amazon Prime Day hits and order volume jumps to 50 times normal levels. Your manual processes break completely. Month-end close runs all reports simultaneously and overwhelms the system.
The company grows from $20M to $50M in revenue, and what worked at the lower volume completely fails at the new scale.
Business impact:
- Failed operations during peak seasons
- Delayed financial reporting
- Emergency hiring during busy periods
- Lost revenue from operational failures
The solution:
- Conduct load testing before go-live using production-scale data volumes, not just sample data
- Use platforms with elastic scaling capabilities that automatically handle volume spikes
- Implement intelligent throttling and rate limit handling that prevents overload
- Choose pricing models that don’t penalize growth with unpredictable transaction-based costs
6. Tool sprawl and integration debt
Multiple point solutions create management overhead and inconsistent governance. Different departments buy their own tools, creating a fragmented, expensive integration landscape that becomes harder to manage over time.
Why this happens:
Teams solve immediate problems with single-purpose tools without considering the long-term architecture. Different departments purchase their own solutions without coordinating with IT. And then some teams are relying on legacy tools “mostly work,” so migration seems too risky or time-consuming to tackle.
The compounding problem:
You end up with a purpose-built data integration tool that only handles ELT, a separate application integration platform, custom scripts filling the gaps, different monitoring systems for each tool, and separate security and compliance processes everywhere.
CFO pressure context:
The post-pandemic shift from “grow at all costs” to profitability has created mandates to consolidate and reduce spending. IT leaders face mounting pressure to do more with less: reduce costs while increasing value to the business.
Business impact:
- Increased total cost of ownership
- Training overhead across multiple platforms
- Inconsistent governance and security practices
- Vendor management complexity
The solution:
- Develop a platform consolidation strategy that supports multiple patterns: application integration, data integration (ELT), reverse ETL, API management, and B2B/EDI
- Look for unified governance, security, and monitoring across all integration types
- Choose predictable pricing models that make budgeting easier
- Reduce to a single vendor relationship, cutting down on contract negotiation and security review overhead
7. Security, compliance, and governance gaps
Spreadsheet-based processes provide no access control, audit trails, or compliance framework. This creates risks for organizations in regulated industries or preparing for IPO, where data governance becomes a critical business requirement.
Why this happens:
Teams prioritize speed over proper controls and lack security expertise. No time gets allocated for compliance requirements, and solutions get deployed without IT oversight through shadow IT initiatives.
Real-world scenarios:
Sensitive financial data sits in uncontrolled spreadsheets that anyone can access or copy. There’s no record of who modified workflows or when changes were made.
You can’t roll back problematic changes when something breaks. Audits fail due to lack of proper documentation, and contractors have access to systems without proper controls in place.
Regulated industry requirements:
SOX compliance is mandatory for financial data. HIPAA governs healthcare information. GDPR and CCPA protect customer data. Organizations preparing for IPO face intense scrutiny of their data controls during due diligence.
Business impact:
- Audit failures that delay or prevent IPO
- Compliance violations and associated fines
- Security breaches that expose sensitive data
- Inability to pursue acquisition opportunities
- Loss of customer trust and reputation damage
The solution:
- Implement role-based access control that ensures only authorized personnel can access sensitive data
- Create complete audit trails showing who modified workflows and when changes occurred
- Use version control and rollback capabilities to recover from problematic changes quickly
- Choose platforms with built-in compliance certifications for SOX, HIPAA, and GDPR
- Establish proper change management workflows that require approval for sensitive modifications
How to overcome data integration challenges
Most data integration failures come down to three mistakes: underestimating how many systems you’ll need to connect, choosing tools that only solve part of the problem, and ignoring error management until it’s too late.
Plan for more complexity than you expect
Before starting, audit every system that contains data you’ll need. Most organizations discover they need seven to ten data sources, not the two or three they initially planned for. Budget for this reality upfront.
Use a platform, not separate tools
Tools that only move data into warehouses force you to buy additional solutions for reverse ETL, application integration, and workflow automation.
This creates exactly the tool sprawl and vendor management headaches you’re trying to avoid. A comprehensive platform handles all these patterns in one place with unified governance and monitoring.
Build in error management from day one
When workflows fail overnight and nobody notices until the CEO asks about missing dashboard data, you have an error management problem. AI-powered platforms automatically handle common issues like API throttling and system downtime without requiring manual intervention.
Data integration challenges: Stop firefighting and start scaling
Data integration challenges are real, but they’re solvable with the right approach—understanding them upfront separates successful implementations from failed projects that waste time, money, and credibility.
The cost of failure is clear. Projects overrun deadlines, business disruption impacts key teams, executive dashboards are missing data, and finance teams are still drowning in spreadsheets.
Meanwhile, with automated data integration solutions like Celigo, you can avoid all seven of these challenges. Your team will get access to real-time insights, prevent common data sync issues, and be able to feel confident in their strategic decision-making.
→ Schedule a demo to see how Celigo can help.