API governance: Best practices for the full API lifecycle

API governance plays a crucial role in enabling organizations to scale and maintain reliable integrations, ensuring APIs remain secure, reliable, and aligned with business goals. Failing to build APIs with clear standards, often leads to workarounds that slow delivery and create brittle connections. Even small changes in one system can disrupt downstream workflows, leading to increased maintenance costs and business risk.
Consistency in API structure enables full API lifecycle management. Standardized endpoints, naming conventions, and data models make APIs easier to reuse across teams. Without this, APIs fragment over time, creating duplicate work, inconsistent security, and governance challenges that undermine long-term reliability.
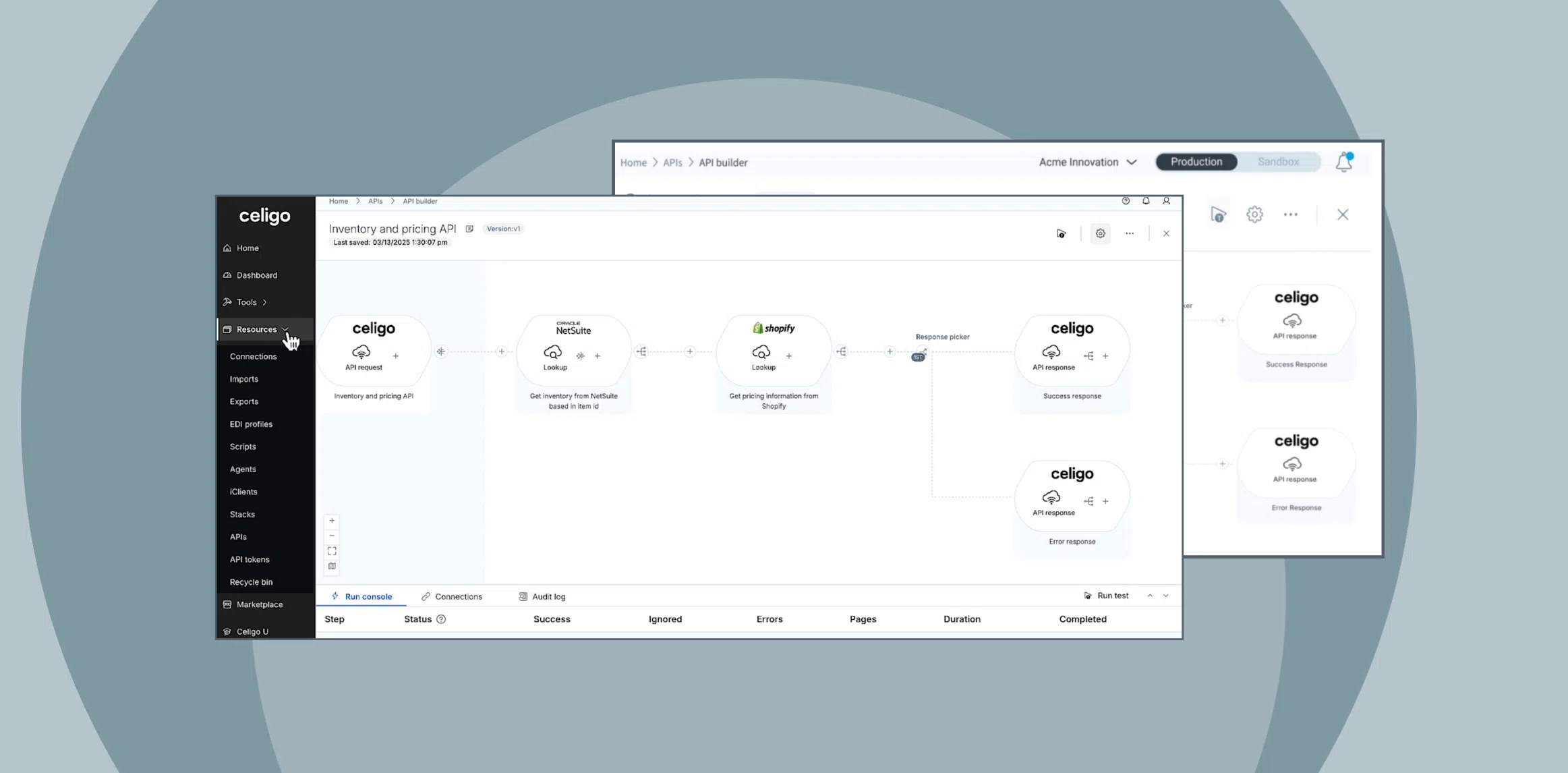
Best practices for building reusable APIs using API builder
Composable APIs are modular by design — built to serve multiple workflows instead of just one. This reduces duplication, ensures consistent logic and error handling, and enables teams to scale faster. As business needs evolve, new workflows can be assembled from existing APIs rather than rebuilt from scratch, improving agility in fast-changing environments.
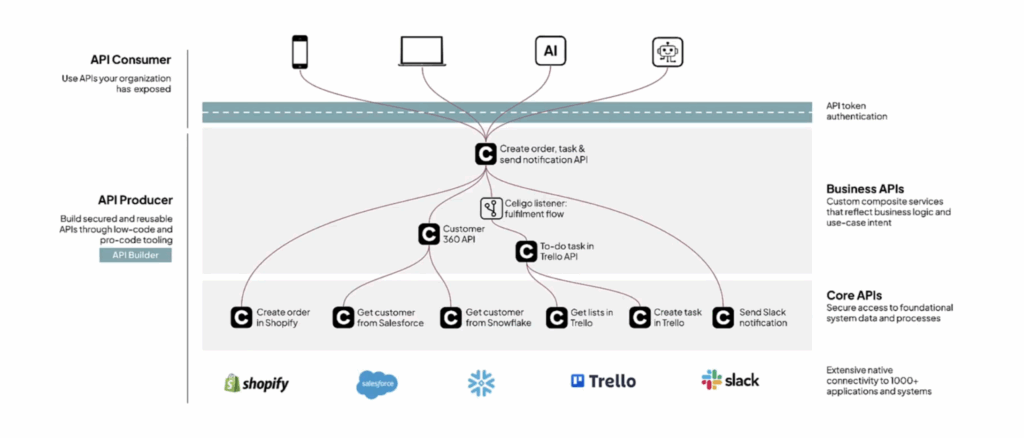
The Celigo APIs Connector brings this to life by letting teams leverage and orchestrate existing APIs within integrations through a unified interface, without custom code or redeployment.
By reusing APIs as building blocks across workflows, Celigo helps organizations accelerate API-led integration, reduce development effort, and maintain consistency across systems.
Along with promoting reusability, effective API governance prescribes how to:
- Build predictably by using consistent URL structures, HTTP verbs, and schema formats.
- Handle errors consistently with clear, predictable responses to improve troubleshooting.
- Support backward compatibility by maintaining older versions until consumers have migrated to newer ones.
- Develop in lower environments (e.g., sandbox or development), conduct peer reviews, and promote through controlled stages before production.
- Review automatically generated OpenAPI specifications to ensure accuracy and consistency across teams.
Securing APIs in API management console
Security is a non-negotiable pillar of API governance, but the depth and nature of security controls should align with an organization’s specific security and compliance requirements. Governance frameworks define how these requirements are enforced consistently across all APIs, ensuring that every integration meets internal and regulatory standards.
APIs should implement strong access controls using OAuth2, JWT, API keys, or mTLS, depending on the sensitivity of the data and compliance obligations. Complementary policies such as IP filtering, data masking, and encryption at rest and in transit further protect sensitive information and reduce the risk of data exposure.
To maintain system reliability and fairness, apply rate limiting and quota policies to prevent overload, control access to high-cost services, and ensure equitable usage across consumers. Logs generated through these controls also serve governance by providing auditable evidence of compliance and surfacing anomalies or violations.
Finally, governance policies should be implemented through consumption plans — standardized bundles that define authentication, quotas, and SLAs per consumer or access tier. This enforces consistency, transparency, and accountability in how APIs are secured and consumed across the organization.
Learn more about securing APIs with customizable security policies and access plans to ensure compliance and reduce exposure risks.
Socializing APIs via developer portal
The socialize phase of API lifecycle management focuses on making APIs discoverable, accessible, and easy to adopt. Publishing APIs in a developer portal makes them accessible across teams and partners while maintaining control through role-based access, subscription workflows, and approval policies. This ensures that APIs are discoverable to the right audiences, without compromising governance boundaries.
Adding categories, labels, and metadata helps developers quickly find APIs, understand their purpose, and determine how they can be safely reused. This reduces duplication of effort, enforces consistent design standards, and promotes standardized, compliant integration practices across business units.
Best practices for monitoring APIs in production
Governance doesn’t end at deployment — it extends into runtime operations. Effective monitoring is a core element of API governance, providing continuous visibility into performance, usage, security, and compliance. The level and depth of monitoring should align with an organization’s governance framework and regulatory obligations, ensuring that every API in production meets defined SLAs and compliance standards.
Recommended governance-driven monitoring practices include:
- Health checks and automated failover to ensure high availability.
- Dashboards to track error rates, traffic spikes, and latency trends in real time.
- Audit trails to log configuration changes, access patterns, and policy violations for compliance reporting.
- Quality metrics and API scorecards to assess governance posture and adherence to standards across APIs.
Continuous API monitoring allows teams to detect anomalies early, such as rising error rates or unexpected latency, and update gateway policies proactively to maintain both performance and compliance.
Integrating these insights into observability tools closes the governance loop, turning runtime data into actionable intelligence that strengthens the overall API ecosystem.
API maintenance best practices
Building APIs with governance in mind reduces issues, but maintenance ensures they remain reliable and relevant. This includes:
- Keeping documentation up to date.
- Applying security policies consistently across dev, test, and production environments.
- Managing access with quotas and usage tiers.
- Using versioning strategies that prevent breaking changes.
- Treating APIs as reusable assets to be standardized and, when appropriate, productized.
A consistent semantic versioning strategy — major.minor.patch (for example, v1.2.5) — should be applied across all APIs. Versions can be tracked either in the URL (e.g., /api/v1/orders) or through metadata.
Older versions should only be deprecated once all consumers have migrated to newer versions.
Evaluate and improve with API quality scoring
Measurement turns governance from policy into practice. Configure API Quality metrics to assess alignment with organizational standards. These metrics reveal where documentation, versioning, or access controls need improvement and demonstrate progress over time.
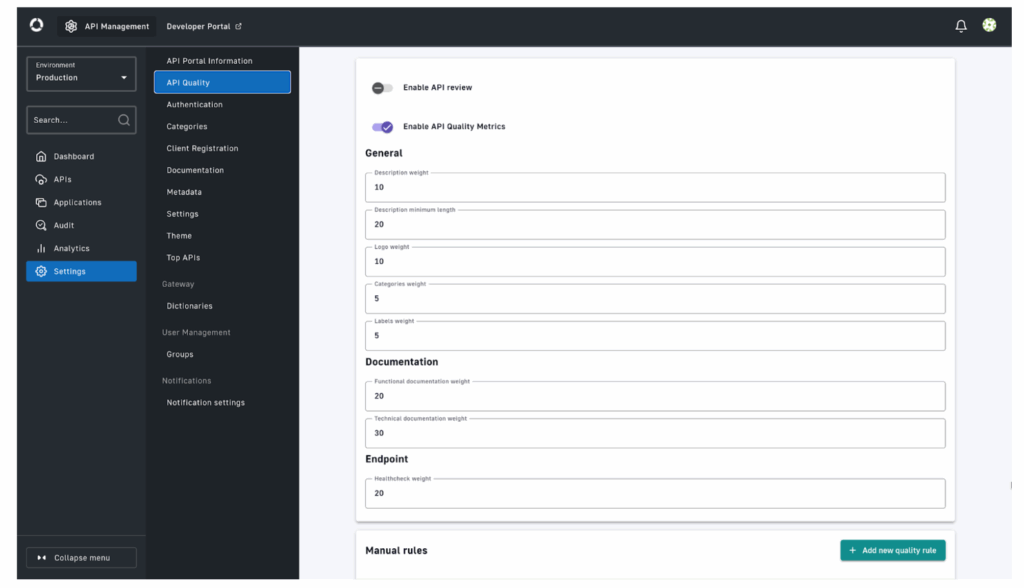
Incorporating quality scoring into governance dashboards provides measurable feedback on both security posture and operational consistency. In the APIs page in the API management console, the quality score can be viewed by users to quickly find out which APIs need attention in order to meet the organization’s quality standards.
Common pitfalls that API governance prevents
From conversations with IT and development teams, these pitfalls appear repeatedly: inconsistent standards, untracked endpoints, security gaps, and duplicated efforts.
Effective API governance provides the structure, automation, and visibility needed to prevent these issues, ensuring that APIs remain secure, scalable, and compliant across their entire lifecycle.
1. Security and compliance risks
- Unsecured or misconfigured endpoints that expose sensitive data due to lack of authentication or encryption.
- Inconsistent policy enforcement across environments leads to compliance gaps or audit failures.
- Overexposed APIs that provide broader access than intended, violating least-privilege principles.
2. Lack of visibility and control
- Shadow APIs (untracked or unregistered endpoints) that bypass governance, creating hidden attack surfaces.
- Inadequate documentation makes APIs difficult to discover, reuse, or maintain.
- Fragmented version management, where outdated or deprecated APIs remain active without monitoring.
3. Operational inefficiencies
- Duplicated functionality across APIs due to poor discoverability and lack of reuse, driving up maintenance costs.
- Unstandardized error handling and response formats complicate troubleshooting and downstream integrations.
- Manual deployment processes without governance checks increase the risk of misconfigurations in production.
4. Performance and scalability challenges
- Unmonitored API performance leading to degraded user experiences or SLA violations.
- Lack of rate limiting or quotas, causing unexpected load spikes or resource exhaustion.
- Inconsistent schema evolution that breaks dependent services during scaling or version updates.
Applying governance across building, securing, socializing, and monitoring reduces these risks and provides a structured framework for scaling integrations reliably.
For IT and system development teams, API governance is not abstract. It directly affects the reliability, scalability, and security of integrations. Without governance, APIs become inconsistent, fragile, and challenging to maintain.
The most effective governance is continuous. When integrated into CI/CD pipelines and observability workflows, it scales naturally with development and operations. The result is an API ecosystem that can grow without introducing brittleness or fragmentation.
FAQ 1: How does Celigo support full API lifecycle management?
Celigo offers comprehensive support for the full API lifecycle, including build, security, publication, monitoring, and versioning, within a unified integration platform.
Through Celigo’s low-code API Builder and integrated API Management, teams can:
-
Build composable APIs with reusable integration logic.
-
Secure endpoints using prebuilt policies such as OAuth2, JWT, API keys, rate limiting, IP filtering, and data masking.
-
Publish APIs via a governed Developer Portal, allowing internal and external users to discover and subscribe.
-
Monitor APIs using built-in analytics dashboards, logging, and API Quality scoring to ensure high performance and compliance.
This end-to-end approach enables consistent and scalable API strategies across applications and teams.
FAQ 2: How does Celigo ensure API governance across teams and environments?
Celigo embeds governance throughout the API management experience to promote consistency and compliance. Key governance features include:
-
Role-based access controls (RBAC) to restrict who can build or modify APIs.
-
Central policy enforcement through the API Management (APIM) console using 40+ configurable policies (e.g., throttling, masking, dynamic routing).
-
Audit trails and version tracking to log every API change.
-
Consistent tagging, naming, and documentation using OpenAPI specifications (OAS).
-
Environment support for development, testing, and production stages, enabling controlled rollouts.
Together, these features help organizations enforce API standards and maintain compliance across departments and projects.
More on Governance and API Policies
FAQ 3: What makes Celigo’s API Builder different from traditional API tools?
Celigo’s API Builder stands out by combining a low-code interface with pro-code extensibility, making it accessible to both developers and business technologists. Unique differentiators include:
-
Build APIs directly from integration flows, making them composable and easily reusable.
-
Clone, modify, and expose APIs rapidly without starting from scratch.
-
Seamless orchestration with Celigo’s iPaaS, allowing users to design and automate complex processes without switching platforms.
-
Publish APIs with full governance via Celigo’s integrated API Management, including the Developer Portal and Gateway for traffic control.
This integrated and user-friendly approach makes scalable API development possible even for non-developers, while still offering the control and depth required by IT teams.
Integration insights
Expand your knowledge on all things integration and automation. Discover expert guidance, tips, and best practices with these resources.