SAP EDI integration for supply chain

Businesses, particularly trading partners, establish a standardized data format to facilitate clear communication — this format is known as Electronic Data Interchange (EDI). EDI is a digital technology used for business-to-business (B2B) transactions and is available in multiple versions, with X12 and EDIFACT being the most common. These transactions, or messages, encompass product details, inventory updates, pricing, purchase orders, sales orders, shipments, invoices, and transfer orders.
Celigo’s B2B Manager for EDI provides built-in tools to integrate, manage, and monitor EDI workflows across all trading partners.
And that’s just the beginning — there’s much more to explore within the platform.
Trading partners overview
Trading partners are the external organizations with which you exchange business documents: suppliers, retailers, manufacturers, marketplaces, logistics providers, and 3PLs. Each partner has its own technical specifications, EDI requirements, and data formats, which can make managing these relationships highly complex, especially when scaling operations.
Whether you’re sending purchase orders to Costco, receiving ASNs from DHL, or syncing invoices with Amazon, EDI ensures these transactions are automated, standardized, and accurate. However, trading partners don’t just “plug in”; each requires configuration, testing, and ongoing monitoring to ensure smooth B2B communication.
Celigo’s B2B Manager simplifies trading partner onboarding and management by providing:
-
Reusable EDI profiles to standardize partner-specific logic
-
Prebuilt templates for common EDI flows (850s, 855s, 856s, 810s, etc.)
-
Centralized error management and monitoring to identify and resolve issues quickly
-
Scalable architecture to support dozens or hundreds of partners simultaneously
With Celigo, managing 10 or 100+ trading partners is no longer a manual IT burden. You get full visibility and control, enabling your team to onboard new partners quickly and scale confidently without third-party bottlenecks.
How does EDI automate my SAP business processes?
There are multiple benefits to integrating systems via EDI.
- Save time: Due to standardization, it is clear what information each trading partner requires and when that is required. The data can be transferred at any time, as often as needed, minimizing the risk of delays.
- Fewer errors: The risk of errors resulting from manual data transmission is much lower due to less human intervention.
- Less manual work: Employees can focus on more important tasks; Redundant tasks can and should be automated to maximize efficiency.
- Scalability: Ability to handle an increased volume of transactions for many trading partners.
EDI workflow example
A trading partner workflow usually contains inbound, outbound, change, and acknowledgment transactions. Each EDI transaction type (X12 and EDIFACT) has its own number and name.
- EDI 832 (EDIFACT PRICAT): Sales Prices and Product Catalog from Supplier to Buyer
- EDI 850 (EDIFACT ORDERS): Purchase Order from Buyer to Supplier
- EDI 860 (EDIFACT ORDCHG): Purchase Order Change from Buyer to Supplier
- EDI 855 (EDIFACT ORDRSP): Order Response and Acknowledgement from Supplier to Buyer
- EDI 856 (EDIFACT DESADV): Advance Shipment Notice (ASN) from Supplier to Buyer
- EDI 846 (EDIFACT RECADV): Goods Receipt notification from Buyer to Supplier
- EDI 810 (EDIFACT INVOICE): Invoice from Supplier to Buyer

Which systems can be integrated?
A supply chain process typically involves multiple parties, each with multiple systems (cloud and on-premise applications) that utilize various connectivity methods (API, EDI, HTTPS, FTP, VAN, AS2, etc.) to communicate with one another. Often, this communication is still done manually by an employee (downloading files, editing documents, sending files, emails, and phone calls).
- SAP ERP systems and others ( SAP Business One / B1, SAP S/4HANA, SAP Business ByDesign, Microsoft Business Central, Oracle NetSuite, Xentral, Sage)
- Procurement systems (e.g., SAP Ariba, SAP Business Network Commerce Automation, Tipalti, Coupa, Procurify)
- Warehouse Management Systems / WMS (e.g., Mintsoft, ShipHero, SEQOS)
- POS / online shop systems (e.g., Shopify, BigCommerce, WooCommerce, Magento / Adobe Commerce Cloud)
- Payment Gateways (e.g., PayPal, Stripe, Braintree, Klarna, Adyen)
- Marketplaces (e.g., Amazon, JD.com, eBay, Zalando, Wayfair, ASOS)
- Retailers (e.g., Amazon, Walmart, Costco, ALDI, Carrefour)
- Third-Party-Logistics (3PLs) (e.g., Amazon, DHL, UPS, Kuehne + Nagel, FedEx, DSV, DB Schenker)
What technologies can be used?
There are multiple ways an EDI message can be transmitted. Let’s call these the communication channels. The usual ones are file-based via an sFTP server, AS2, VAN, REST APIs, or SOAP-based web services. Celigo’s B2B Manager can connect to all of these and enable communication between the different trading partners’ systems.
Is it always EDI?
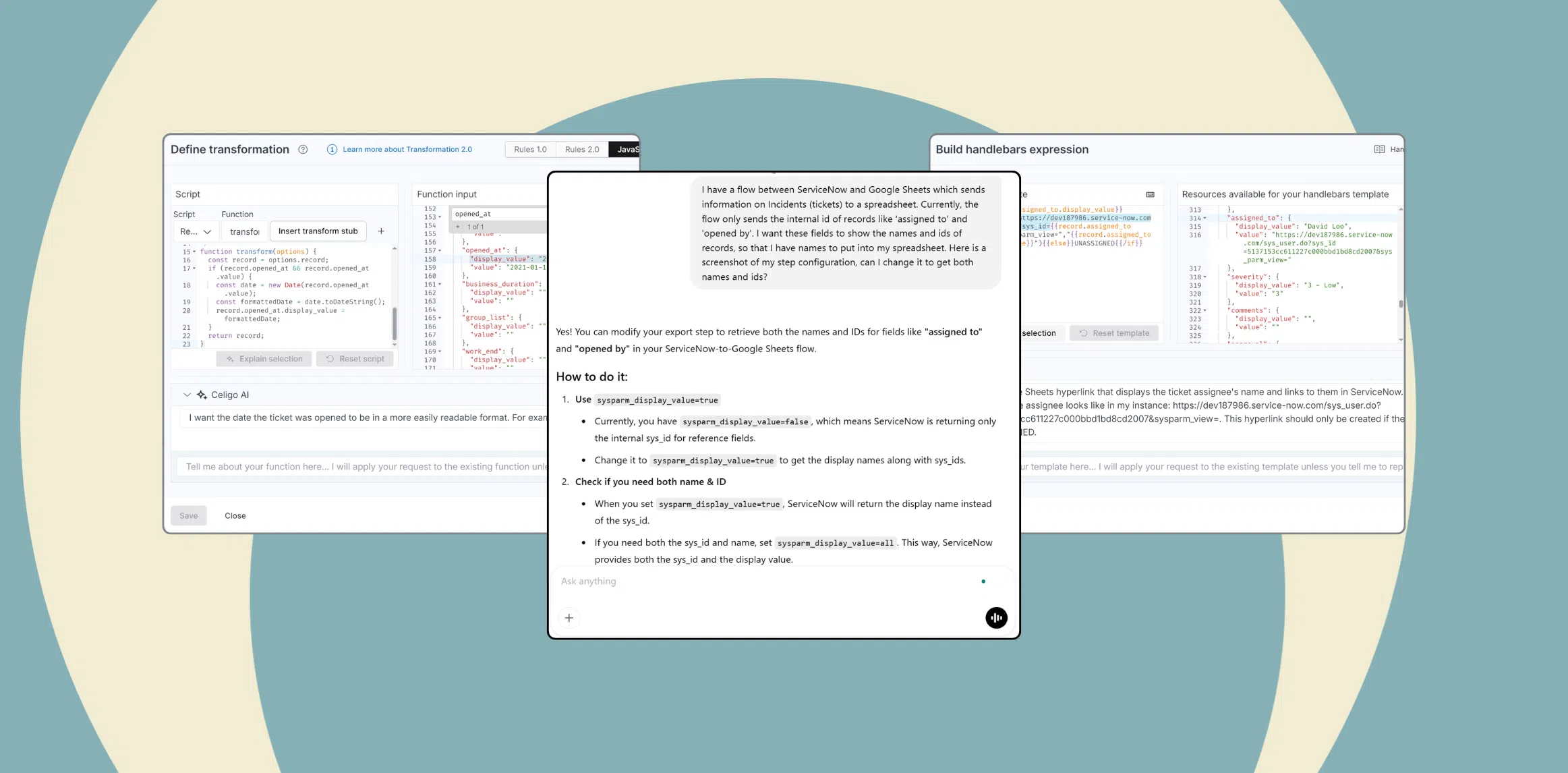
EDI is only one of many specifications or mediums that can be used for automated data exchange. Other examples are XML, CSV files, and JSON. In some use cases, it is required to transform the data or translate it from one file type into another between the export and the import, which can also be done on integrator.io.
B2B Manager for EDI
Celigo’s B2B Manager for EDI allows you to manage all of your EDI integrations in one place.
The functionalities include:
- Building and running integrations and automating supply chain processes.
- Analyzing runs and improving the performance.
- Getting notified about errors and managing them on one centralized platform.
- Collaborating with multiple users, documenting, and managing your integration life cycle.
- Managing resources to speed up your building process.
- Leveraging pre-built integrations and trading partner profiles for a quick setup.
Learn more about how modern EDI integration improves procurement and supply chain efficiency across ERP systems.
How to get started
Here are the first steps for your SAP EDI integration:
Get in contact with your trading partners and Celigo.
- Create a process diagram that shows the actions, roles, and systems involved in the process.
- Analyze what can be automated and create a roadmap.
- Ask for process documentation, technical references, and specifications from all parties involved.
Optional: If needed, get help from Celigo professional services or one of Celigo’s certified partners, or become a Celigo builder yourself using Celigo University.
Integration insights
Expand your knowledge on all things integration and automation. Discover expert guidance, tips, and best practices with these resources.