Modern EDIFACT EDI integration for any ERP

EDIFACT (Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport) is the international standard for electronic data interchange, widely used across Europe and the Asia-Pacific region. It defines how businesses exchange structured B2B documents such as purchase orders, invoices, and dispatch advice.
Although the standard is universal, implementations vary by trading partner and system. Many organizations still rely on managed service providers and brittle mappings that require heavy development effort. As a result, every new trading partner feels like a custom project, and every change introduces risk; IT is left managing a growing web of partner-specific requirements that is difficult to scale.
Here, we’ll discuss how a modern approach to EDI unifies EDI and ERP integration, supports multiple formats, enables real-time monitoring, and utilizes reusable trading partner profiles to reduce complexity while providing IT with full control.
Why legacy EDIFACT EDI approaches don’t scale
Two common legacy models create significant operational drag:
Managed EDI services
- Visibility is limited; mappings and logic are hidden behind support tickets
- SLA issues often surface only after delays
- Even minor modifications (code lists, field formatting, qualifiers) require vendor coordination
- Implementation timelines depend on vendor’s bandwidth and expertise
Self-service EDI on legacy middleware
- Each partner has unique requirements, requiring a new implementation project and separate testing
- Updates are risky and slow, making routine compliance changes burdensome
- Documentation tends to be inconsistent or lacking
Neither approach supports agility. Adding a trading partner shouldn’t be a months-long initiative. Modifying a validation rule shouldn’t risk breaking other flows. EDI shouldn’t require external vendor dependencies or black boxes.
From managed to modern EDIFACT EDI integration
Modern EDI solutions treat EDIFACT as a structured data format rather than a legacy protocol. With the right integration solution, EDI becomes part of the broader automation strategy, shifting from a maintenance-heavy system to an extensible, in-house capability.
A modern, scalable EDI solution should:
-
Connect directly to trading partners and ERP systems, including SAP, Microsoft Dynamics 365, Oracle NetSuite, and others
-
Support global standards such as EDIFACT and X12, and multiple protocols including AS2, FTP/SFTP, VAN, and APIs
-
Enable no-code/low-code mapping, trading partner-specific profiles, and transformation tools to reduce manual effort
-
Provide real-time visibility with monitoring, control number traceability, and proactive error handling
With this foundation, EDI becomes an integrated part of your business processes, not an isolated toolset.
Automate inbound and outbound EDIFACT workflows
Modern EDI integration requires automation across the entire document lifecycle, covering both inbound and outbound transactions.
By automating how documents are received, translated, and delivered, organizations can ensure accurate, timely data exchange without manual intervention.
Inbound EDIFACT documents
- Received via AS2, FTP/SFTP, VAN, or API
- Parsed using a partner-specific EDIFACT profile
- Converted to structured formats (JSON/XML)
- Routed into ERP, OMS, or WMS as sales orders, shipments, or invoices
Outbound EDIFACT documents
- Triggered by internal system events (e.g., sales invoice creation)
- Mapped to canonical formats
- Transformed into EDIFACT using partner-specific rules
- Transmitted securely with logging and error-handling
Common transaction sets include ORDERS (purchase order), ORDCHG (order change), DESADV (dispatch advice), and INVOIC (invoice).
Automation ensures timely, accurate data exchange without manual touchpoints or downstream delays.
Use reusable EDIFACT partner profiles
Each trading partner has its own quirks — custom qualifiers, non-standard segments, and preferred protocols. Instead of building one-off integrations, modern platforms use profile-based architecture to decouple partner configuration from core flows.
With reusable profiles, you can:
- Store mapping templates, segment definitions, validation rules, and transport settings per partner
- Reuse flows across partners by swapping profiles, not rebuilding logic
- Standardize operations while supporting partner-specific exceptions
This makes onboarding faster, reduces maintenance, and ensures processing consistency.
→ Read more: Create EDI profiles for EDIFACT flows
Real-time EDIFACT monitoring and error handling
Legacy EDI systems often lack transparency. A document fails, and no one knows until a retailer sends a chargeback.
Modernized EDI changes that with centralized monitoring and built-in error management.
Teams can:
- Track every inbound and outbound transaction
- View acknowledgments (e.g., CONTRL) and delivery confirmations
- Filter by partner, document type, or control number
- Get alerted on issues like missing segments or failed transformations
Exception handling is embedded in the flows, allowing for automated retries, conditional logic paths, and alerting through email, or other systems that can be integrated—without requiring support tickets.
ERP-agnostic EDIFACT EDI integration
In many organizations, EDI remains isolated, managed on separate systems by dedicated teams that often operate on their own schedules. Modern solutions break down these silos by consolidating EDI and ERP integration into a unified environment.
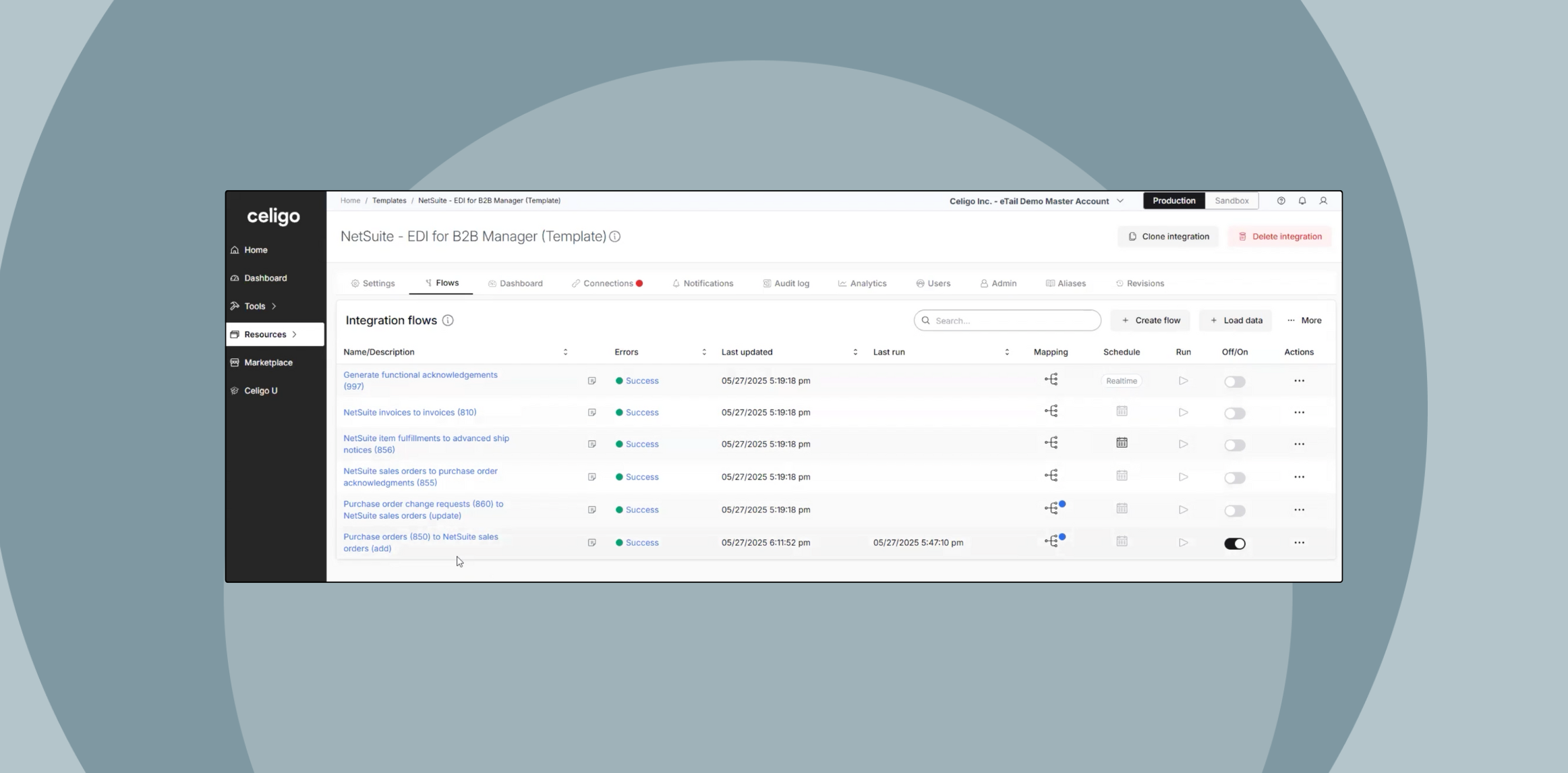
Celigo’s B2B Manager for EDI supports EDIFACT and ANSI X12-based EDI, API, and application integrations within one solution, providing:
-
Centralized visibility and control
-
Centralized governance
-
Unified automation
Whether you run SAP, Oracle NetSuite, Microsoft Dynamics, or a combination of systems, your EDI operates in conjunction with the rest of your integration landscape.
Scaling EDI without adding IT overhead
This approach shifts IT’s role from maintaining EDI to enabling operations. Instead of managing vendors, IT teams can define reusable integration patterns, manage configurations, and rely on automation to handle execution.
Key benefits include:
-
Fewer vendor dependencies
-
Reduced IT overhead
-
Faster time-to-value
-
Lower operational risk
-
Scalable governance
Because EDI is integrated into your broader solution, your team retains full control from implementation through compliance.
Modernize EDIFACT EDI
Celigo’s B2B Manager for EDI provides a modern, self-service alternative to legacy EDI systems. It eliminates manual syncs, file transfers, and external vendor queues by enabling direct, automated workflows between trading partners and your ERP, without custom code.
B2B Manager for EDI includes:
-
Prebuilt EDIFACT documents
-
Self-service mapping and transformation tools
-
Reusable trading partner profiles
-
Monitoring, error visibility, and control number traceability
-
Unified support for both EDI and API-based workflows
-
A single dashboard to manage all B2B integrations
Ready to eliminate EDI silos and take full control of your B2B workflows?
Schedule a personalized demo to see how self-service EDI integration can streamline operations, reduce costs, and scale with your business.
Integration insights
Expand your knowledge on all things integration and automation. Discover expert guidance, tips, and best practices with these resources.